What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Grave’s Disease (due to Autoimmune Thyroiditis)
- Hashimoto's Disease (due to Autoimmune Thyroiditis)
- Struma Lymphomatosa (due to Autoimmune Thyroiditis)
What is Autoimmune Thyroiditis? (Definition/Background Information)
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis is a chronic inflammatory disorder, characterized by abnormal white blood cells and antibodies attacking the thyroid gland. Middle-aged women are reported to be more susceptible to Autoimmune Thyroiditis
- In Autoimmune Thyroiditis, an individual’s thyroid gland is attacked by his/her own immune system. It is a progressive disease that destructs the thyroid hormone function, and eventually results in thyroid hormone deficiency (hypothyroidism). Autoimmune Thyroiditis is the common cause of primary hypothyroidism
- Some risk factors for developing this disorder include the female gender, excess consumption of iodine, use of certain drugs, and having had viral infections
- The symptoms of Autoimmune Thyroiditis may include enlarged neck, hair loss, weight gain, constipation, and menstrual abnormalities in women. The condition may potentially lead to autoimmune disorders involving other organs and thyroid cancer, in some cases
- Thyroid hormone replacement is the most effective treatment for Autoimmune Thyroiditis. There are no known preventative measures for this condition. However, the condition may remain stable for many years without worsening of the signs and symptoms, thus making the treatment options successful
Who gets Autoimmune Thyroiditis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis may occur in adolescent and young women. But, it is more prevalent in women between 40-60 years of age
- The disorder can affect both genders. However, it is reported that women are 7-times more prone to developing the condition than men
- All racial and ethnic groups may be affected
What are the Risk Factors for Autoimmune Thyroiditis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
Some risk factors known to be associated with Autoimmune Thyroiditis include:
- Individuals with a family history of the disorder, specifically close relatives with Autoimmune Thyroiditis or other autoimmune conditions
- Women with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Female gender, particularly middle-aged women
- Individuals with congenital (chromosomal) disorders such as Turner syndrome, Down syndrome, and Klinefelter syndrome
In susceptible individuals, researchers have identified potential environmental factors that the disorder can be attributed to, such as:
- Excess consumption of iodine may inhibit thyroid hormone synthesis
- Certain drugs
- Viral infections
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases one's chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Autoimmune Thyroiditis? (Etiology)
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis is caused by the dysregulation of an individual’s own immune system. The immune system creates antibodies, which destroy the thyroid gland, resulting in thyroid hormone deficiency and manifestations of symptoms
- Scientists have discovered a genetic component to the disorder. Mutations in two genes, one each on chromosome 2 and 8, appear to be necessary for manifestation of the symptoms
- In many cases, Autoimmune Thyroiditis is believed to be the cause of primary hypothyroidism
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Autoimmune Thyroiditis?
In many cases, during the early stages of Autoimmune Thyroiditis, there are no signs and symptoms. Then, as it progresses, it may cause hyperthyroidism with associated signs and symptoms that include:
- Sleeping difficulties including insomnia
- Excess sweating and intolerance to heat
- Increased to excessive hunger
- Irritation, restlessness
- Protrusion of the eyes
- Menstrual abnormalities; menstruation may be irregular or short
- Abnormal heartbeat rate including rapid heart rate
- Sudden weight loss
When the condition is more severe it leads to hypothyroidism, and the signs and symptoms associated with this condition may include:
- Enlarged or swollen thyroid gland; small or shrunken thyroid gland (late in the disease)
- Difficulty concentrating or thinking
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Dry skin
- Hair loss, which may be in excess while showering
- Constipation or difficult bowel movements
- Weight gain that may be slow and gradual
- Heavy and irregular periods (in women)
- Abnormal sensitivity to cold; the affected individuals may not tolerate cold very well
How is Autoimmune Thyroiditis Diagnosed?
Autoimmune Thyroiditis develops slowly, so it may not be clinically apparent for many months or years. The diagnosis of this disorder generally involves the following tests and procedures:
- Complete evaluation of medical history and a thorough physical examination
- During examination, a healthcare provider may pay special attention to the following:
- An enlarged thyroid in front of the neck
- The signs and symptoms of the individual
- Blood tests to evaluate the levels of:
- T3 and T4; thyroid hormones produced in the thyroid gland
- Serum TSH (thyroid stimulating hormone)
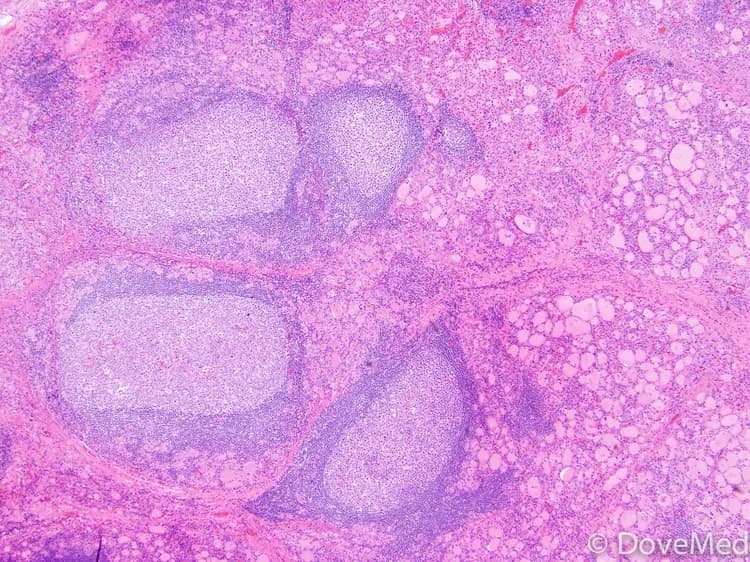
- Antithyroid peroxidase antibody (Anti-TPO); antibodies against thyroid peroxidase, an enzyme in the thyroid gland
- Antithyroglobulin antibody; antibodies interacting with thyroglobulin, a protein found on the thyroid cells
- Ultrasound scans of the thyroid gland
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) biopsy or core biopsy of the thyroid gland
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Autoimmune Thyroiditis?
The potential complications of Autoimmune Thyroiditis may include:
- Simultaneous development of other autoimmune disorders
- Development of thyroid cancer (in some rare cases)
How is Autoimmune Thyroiditis Treated?
The treatment of Autoimmune Thyroiditis depends on the presence or absence of hypothyroidism (a deficiency in thyroid hormone production).
- When hypothyroidism is absent: Patients are generally monitored for the progression of the disease and development of hypothyroidism
- When hypothyroidism is present: Thyroid hormone replacement therapy may be considered
How can Autoimmune Thyroiditis be Prevented?
- Currently, no effective preventive methods have been reported for Autoimmune Thyroiditis
- However, early detection, prompt treatment, and regular monitoring of the condition can help combat the disorder and keep its progression under control
What is the Prognosis of Autoimmune Thyroiditis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis can remain stable for many years with treatment; hence, the treatment provided is usually deemed successful
- The prognosis of the disorder is generally good with proper treatment and regular check-ups
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Autoimmune Thyroiditis:
Healthcare providers generally term this condition as Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis, if there is a swollen thyroid gland associated with it. If the thyroid gland is shrunken, then the condition is called Atrophic Thyroiditis.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.