What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Amebic Dysentery
- Entamoebiasis
- Infection due to Entamoeba histolytica
What is Amebiasis? (Definition/Background Information)
- Amebiasis is an infection caused by an amoeboid-protist, Entamoeba histolytica (single-celled microorganism). The infection is characterized by the presence of these protists in the gastrointestinal tract
- Amebiasis or Amebic Dysentery, is caused by exposure to infected feces. This may occur either through contaminated water, or through hand-to-mouth route
- Therefore, the prevalence of this disease is higher in those locations with poor sanitary conditions, like those found in developing nations, and which lack sufficient sources of clean and filtered water
- The amoeba, also thrives in warm moist conditions, favoring a longer lifespan without a host. This is one of the reasons, why Amebic Dysentery is concentrated in the tropical regions
- Many people are infected, without showing any signs and symptoms of the disease. These individuals are called the carriers of Amebiasis. Since, such carriers do not exhibit any signs and symptoms of the infection; it makes it difficult to track the number of individuals, carrying the disease-causing agent
- Blood tests and/or stool tests may be used to diagnose the condition, which can be treated using medications. The outcome on proper treatment, for Amebiasis, is generally good
Who gets Amebiasis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Individuals of all age, race/ethnicity, and both sex, can be infected by Amebiasis
- Due to the nature of the disease-causing protist, individuals living in areas that lack adequate sanitation (mostly tropical developing countries), are far more prone to an onset of the disease
What are the Risk Factors for Amebiasis? (Predisposing Factors)
Following are the risk factors of Amebiasis:
- Exposure to contaminated water
- Poor hygiene, lack of proper sanitation facilities: Travelling to tropical areas with unsanitary conditions, increases the likelihood of exposure to this disease
- Young or elderly people, who have poor immune function: Such individuals are more likely to develop this disease, because their immune systems are weaker
Consequently, individuals who lack proper nutrition may have weaker immune systems, and are more likely to develop Infection due to Entamoeba histolytica, when they consume contaminated food/water.
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Amebiasis? (Etiology)
Amebiasis infection is caused by the microorganism Entamoeba histolytica, an amoeboid-protist. Upon ingestion, E.histolytica multiplies along the gastrointestinal tract.
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Amebiasis?
In some individuals, the Amebiasis infection is asymptomatic, while in others, adverse signs and symptoms may be experienced. Such symptoms may take a few days to several weeks to occur, after infection.
These could include:
- Diarrhea
- Dysentery
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Excessive gas
- Rectal pain, occurring with bowel movement
- Vomiting
It is possible for the protist to enter the circulatory system and continue to invade other organs, such as the liver, lungs, and sometimes the brain.
How is Amebiasis Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Amebiasis would include:
- Physical exam with evaluation of medical history
- Cysts found in stools: Cysts expelled in the feces can lead to a diagnosis of Amebiasis. Feces can often contain living motile forms of the amoeba, which may be detected under microscopic inspection. However, these cysts are not expelled with constant frequency. Also, their appearance can be similar to those made from the non-virulent Entamoeba coli, which may cause a misdiagnosis
- Serological tests for the presence of antibodies in blood: Two weeks after infection, it is possible to detect the presence of antibodies in an infected patient’s blood. The antibodies are much more prevalent in those individuals, who have developed a liver abscess due to the disease. Diagnosis, via inspection of the feces becomes significantly harder, once infection has spread outside the GI tract
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Amebiasis?
Complications from Amebiasis could include:
- Liver abscess
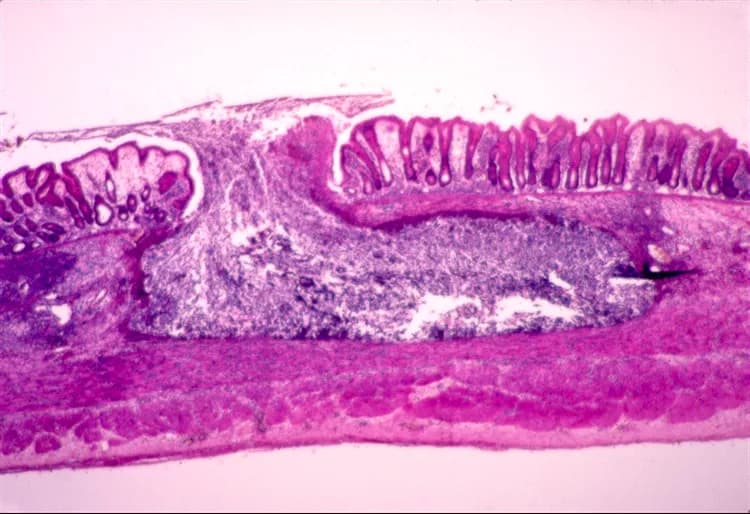
- Ulceration of gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which occasionally can lead to perforation
- Amoebomas: These are tumor-like masses that occur in a variety of organs
Typically, less than 16% of infected individuals develop ulcers in the GI tract, and even less have the infection spread extra-intestinally. However, spread of the amoeba, can lead to very rare complications of the liver, lungs, and brain. Additionally, the urinary tract may also be involved, more so in females.
How is Amebiasis Treated?
Treatment of Amebiasis could include:
- Treatment using drugs, called amoebicides, are commonly and effectively used, to kill internal amoebas
- In case of severe dehydration, either oral fluids, or intravenous fluids may be given
- In case of a GI perforation, surgical procedures may be required
How can Amebiasis be Prevented?
Helpful tips to prevent Amebiasis are:
- Maintain proper hygiene
- Wash hands with soap, before meals
- Boil or use iodine, to disinfect drinking water
- Wash vegetables/fruits prior to consumption
- If you are visiting tropical areas, take clean food and water; especially if you are in regions that lack proper hygiene
- Avoid direct anal contact that may result in transmission of the amoeba, through the feco-oral route
What is the Prognosis of Amebiasis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- The prognosis of an individual with Amebiasisis generally good with proper treatment
- A subsequent check of the individual’s infection status after treatment may ensure complete eradication of the amoeba
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Amebiasis:
The FDA has published a book titled, ‘Bad Bug Book’, which contains information about Entamoeba histolytica and other infectious diseases.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.