What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- Alpha-Mannosidase B Deficiency
- Lysosomal Alpha-D-Mannosidase Deficiency
- Mannosidosis
What is Alpha-Mannosidosis? (Definition/Background Information)
- Alpha-Mannosidosis is a rare, genetically inherited disorder characterized by low alpha-D-mannosidase enzyme activity
- The disorder can affect many, different organs and tissues in the body, resulting in mental disability, as well as physical deformities
Two types of Alpha-Mannosidosis are known to exist:
- Early-onset occurs during the individual’s infancy; it progresses rapidly, and is typically fatal
- Late-onset occurs during the individual’s adolescence or early adulthood, and progresses slowly
Who gets Alpha-Mannosidosis? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- Alpha-Mannosidosis is typically diagnosed in children under the age of 10 years, or in individuals in their early adulthood
- Worldwide, the condition is believed to occur in 1 in 500,000 individuals
- The disorder can affect both males and females
What are the Risk Factors for Alpha-Mannosidosis? (Predisposing Factors)
Common risk factors of Alpha-Mannosidosis include:
- Family history of the disorder
- Respiratory infections
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Alpha-Mannosidosis? (Etiology)
- Alpha-Mannosidosis is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder caused by a mutation on the MAN2B1 gene
- Typically, this gene provides the coding for the production of the alpha-D-mannosidase enzyme; an enzyme, which has an important role to play in the lysosomes (a cell component), to break down mannose (sugar molecule in oligosaccharides) so that they may be digested and recycled
- When mutations are present on the MAN2B1 gene, the alpha-D-mannosidase enzyme is not produced correctly, which interferes with the body’s ability to break down mannose. This leads to accumulation of oligosaccharides (complex carbohydrate of sugars) in the lysosomes, which causes cell malfunction and death
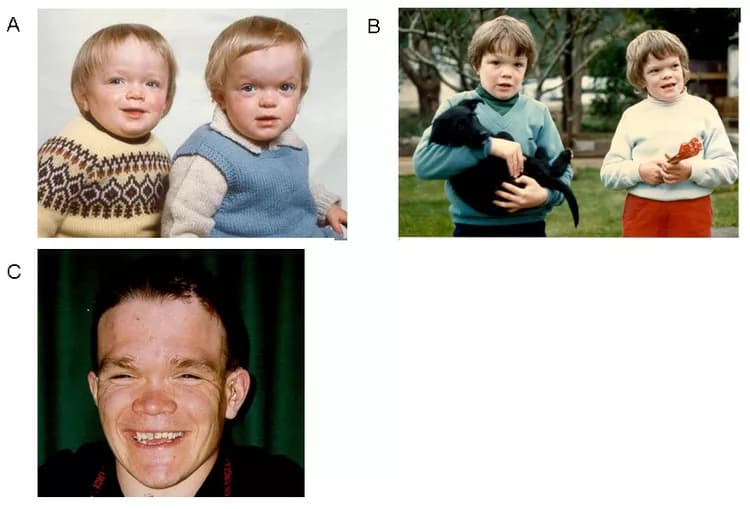
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Alpha-Mannosidosis?
Signs and symptoms of Alpha-Mannosidosis include:
- Intellectual disability
- Reduced bone density, muscular weakness
- Spine deformations
- Bowed legs
- Prominent forehead, low hairline
- Large ears, hearing loss
- Widely spaced teeth, large tongue
- Ataxia (difficulty with movement coordination)
- Cataract
- Depression
- Hepatosplenomegaly (enlarged liver)
- Hydrocephalus (fluid build-up in brain)
How is Alpha-Mannosidosis Diagnosed?
Several tests used by medical professionals to diagnose Alpha-Mannosidosis include:
- Physical exam with medical history
- Blood tests, to measure enzyme activity
- Urinalysis (urine analysis)
- Oligosaccharide analysis, to measure oligosaccharide presence in the body
- Mannosidase enzyme analysis to measure enzyme presence
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Alpha-Mannosidosis?
- Most complications from Alpha-Mannosidosis arise with the early-onset form
- During the first year of life, infants with the genetic condition can suffer from complications that impact motor skills, immune system functioning, and facial feature development
- Bacterial infections and joint problems may also arise as a result of Alpha-Mannosidosis
How is Alpha-Mannosidosis Treated?
Due to the genetic nature of Alpha-Mannosidosis, there is no treatment to cure the condition. Instead, treatment options exist to help ease the signs and symptoms of the disorder.
- Physiotherapy helps in treating the physical deformities that occur as a result of Alpha-Mannosidosis. It is especially important if bone density is reduced and spinal deformities are observed
- Surgery is often suggested to treat skeletal and facial abnormalities
How can Alpha-Mannosidosis be Prevented?
- Currently there are no specific methods or guidelines to prevent Alpha-Mannosidosis genetic condition
- Genetic testing of the expecting parents (and related family members) and prenatal diagnosis (molecular testing of the fetus during pregnancy) may help in understanding the risks better during pregnancy
- If there is a family history of the condition, then genetic counseling will help assess risks, before planning for a child
- Active research is currently being performed to explore the possibilities for treatment and prevention of inherited and acquired genetic disorders
- It is important that there is an early intervention to properly treat the symptoms of the disorder. Only this can ensure that the children with Alpha-Mannosidosis, reach their highest potential and capacity
What is the Prognosis of Alpha-Mannosidosis? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
- Most infants, who suffer from Alpha-Mannosidosis, do not survive beyond the age of 10 years
- Milder cases that become apparent during early adulthood are usually more manageable. These individuals have a higher chance of living, until the age of 50 years (at least), with proper symptomatic treatment
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Alpha-Mannosidosis:
Autosomal recessive: Autosomal recessive conditions are traits or disorders that occur when two copies of an abnormal gene have been inherited on a non-sex chromosome. If both parents have an autosomal recessive condition, there is a 100% likelihood of passing on the mutated genes to their children. If, however, only one mutant copy of the gene is inherited, the individual will be a carrier of the condition, but will not be present with any symptoms. Children born to two carriers, have a 25% chance of being homozygous dominant (unaffected), a 50% chance of being heterozygous (carrier), and a 25% chance of being homozygous recessive (affected).
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.