What are the other Names for this Condition? (Also known as/Synonyms)
- AA (Alopecia Areata)
- Alopecia Areata Totalis
- Alopecia Areata Universalis
What is Alopecia Areata? (Definition/Background Information)
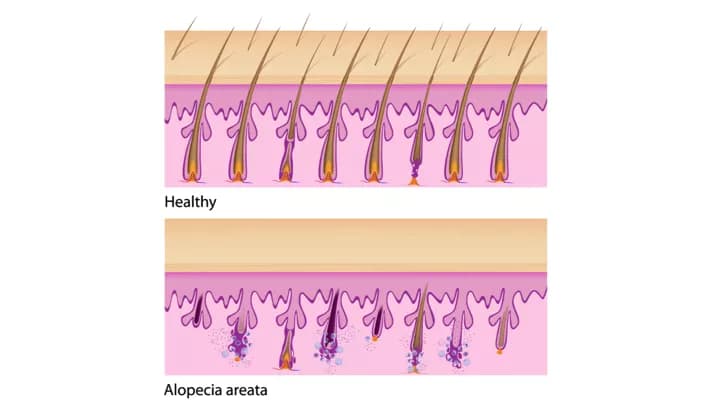
- Alopecia Areata (AA) is loss of hair in patches, often in round or oval patterns, from any hair-bearing area of the body. Several different conditions may cause the occurrence of hair loss
- There are two other subtypes of Alopecia Areata based on their distribution and extent:
- Alopecia Areata Totalis: It is a severe form of Alopecia Areata, which affects the entire scalp. All scalp hair is lost in this type of AA
- Alopecia Areata Universalis: It is the most severe and rarest form of Alopecia Areata, where all hair from all hair-bearing regions of the body, including the scalp, is lost. This may occur independently or following a localized loss of hair
- Alopecia Areata is a medically benign disease, but it may pose great emotional and psychological stress to the affected individual and their family members
- Currently, there are no methods to prevent Alopecia Areata. The condition is treated using medications. Nevertheless, in most individuals, the prognosis is good. They grow back the lost hair within a year or so
Who gets Alopecia Areata? (Age and Sex Distribution)
- The worldwide prevalence of Alopecia Areata (AA) is 0.1-0.2%, with a 1.7% lifetime risk. AA may occur at any age; the peak incidence is in the 15-29 years’ age group
- Alopecia Areata is the most common form of Alopecia seen in the pediatric population. Even congenital cases of AA have been reported
- Both male and female genders are equally affected
- The condition is more common in individuals with chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome
What are the Risk Factors for Alopecia Areata? (Predisposing Factors)
The following are the risk factors for Alopecia Areata:
- A positive family history of the condition
- Certain chromosomal disorders such as Down syndrome
- Individuals with increased stress are at a risk for Alopecia Areata
It is important to note that having a risk factor does not mean that one will get the condition. A risk factor increases ones chances of getting a condition compared to an individual without the risk factors. Some risk factors are more important than others.
Also, not having a risk factor does not mean that an individual will not get the condition. It is always important to discuss the effect of risk factors with your healthcare provider.
What are the Causes of Alopecia Areata? (Etiology)
The exact cause of Alopecia Areata is not well-understood. But various hypotheses related to Alopecia Areata etiology are proposed. These include:
Autoimmune disorders:
- This hypothesis is that the hair follicles and other components of the hair cells are targeted by autoantibodies and activated T- lymphocytes (T-helper cells are more involved than T-suppressor cells)
- The outer root sheath is the part of the hair cell that is targeted most frequently by the antibodies. The other hair cell components, such as the inner root sheath, matrix, and hair shaft (to a lesser extent), are also targeted
- Clinical evidence suggests that certain autoimmune conditions, such as thyroid diseases and vitiligo, may have some association with Alopecia Areata
Genetic predisposition:
- This hypothesis is based on the fact that AA is severe in twins and patients with Down syndrome (trisomy of chromosome 21)
- There is often a family history of the disease noted
- It is believed that many genes (polygenic) are likely involved in this disease process
Stress:
- An increased correlation is observed between individuals with increased traumatic life events, especially in childhood, and Alopecia Areata
- Individuals may report a major emotional stress prior to onset of the disease
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Alopecia Areata?
The signs and symptoms of Alopecia Areata include:
- Patchy loss of hair, most commonly on the scalp, but that may occur in any hair-bearing area of the body
- Regions of hair loss are usually asymptomatic, but sometimes may present with burning or itching sensations
- The presence of autoimmune disorders such as vitiligo (a skin condition) and thyroid disease
- Tapering of the hair shaft near the skin (like an exclamation mark)
- Hair follicles near the hair loss patch are easily ‘pluckable’, which indicates a disease activity
- Finger and toe nails may be involved, resulting in pitting, sandpaper-like nails, and/or spooning of the nails
How is Alopecia Areata Diagnosed?
A diagnosis of Alopecia Areata (AA) can be made by studying the clinical signs and symptoms. Following are the diagnostic tools that may be used:
- A thorough physical examination and complete medical history are very crucial to establishing a diagnosis
- A skin biopsy is not needed in most cases
- Dermoscopy is a diagnostic modality, which in Alopecia Areata, most commonly identifies yellow spots in the areas of hair loss. Yellow spots represent the keratinocytes in the hair follicles and sebum
Many clinical conditions may have similar signs and symptoms. Your healthcare provider may perform additional tests to rule out other clinical conditions to arrive at a definitive diagnosis.
What are the possible Complications of Alopecia Areata?
There may be significant psychological burden associated with Alopecia Areata. Generally, there are no physical health related complications noted.
How is Alopecia Areata Treated?
There is no universal treatment for Alopecia Areata (AA); however, numerous treatment options are available with varying effectiveness. Most recommendations are based on clinical experience and case studies.
Numerous treatment algorithms have been practiced. A more common example is given below:
- For individuals below 10 years old: Minoxidil 5% solution +/- topical steroid (or topical Anthralin)
- For individuals above 10 years old:
- If less than 50% involvement of scalp is present: Intralesional steroids (steroid injected at the site of hair loss) +/- Minoxidil 5% solution +/- topical steroid +/- Anthralin
- If greater than 50% involvement of scalp is present: Topical immunotherapy - squaric acid dibutylester (SADBE) and diphencyprone (DPCP). If there is an improvement, immunotherapy can be continued as needed. If there is poor to no improvement seen, then Minoxidil 5% solution +/- topical steroid or Anthralin or PUVA (Psoralen + UVA light treatment)
- There are reports that injections of a patient’s own platelet rich plasma (PRP) can improve AA
- Ointments formulated to contain Tyrosine Kinase 2 inhibitors are reported to improve AA. However, the cost of the medication limits the use in AA
- In many new-onset cases with localized hair loss, there is spontaneous re-growth of hair within a year or so
- Sometimes, based on the healthcare expert’s evaluation, no treatment is initiated
- Other options include: Camouflaging the condition using hair patches/pieces, styling products, or make-up
How can Alopecia Areata be Prevented?
As the disease onset and course are unpredictable, currently there are no methods to prevent Alopecia Areata.
What is the Prognosis of Alopecia Areata? (Outcomes/Resolutions)
Alopecia Areata (AA) is a hair condition with no clearly established cause and preventative methods.
- However, in most individuals, only a few focal areas of body or scalp hair loss are observed; a spontaneous re-growth of hair usually occurs within 1 year. Hence, the prognosis of Alopecia Areata is generally good in many cases
- Factors that adversely affect the prognosis include young age of the individual at onset of AA, the form of AA one is affected with (the more severe the form, the poorer is the prognosis), and the presence of any nail abnormalities
Additional and Relevant Useful Information for Alopecia Areata:
Hair transplant is a surgical procedure designed to improve baldness. In this procedure, hair and skin from the side and back of the head (called graft), is relocated to the front balding areas.
The following article link will help you understand hair transplant surgical procedure:
http://www.dovemed.com/common-procedures/procedures-surgical/hair-transplant/
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals


0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.