Background Information:
What are the other Names for the Procedure?
- Computerized Tomography - Pediatric
- Pediatric CT Scan
- X-ray Computed Tomography - Pediatric
What is Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure? (General Explanation)
- CT (Computed Tomography) scanning, also referred to as a CAT scan, is a noninvasive test used to diagnose and treat medical conditions, by combining a special X-ray machine with computers, to produce images of the body insides
- CT scanning provides more details of soft tissues, blood vessels, and internal organs, than a regular X-ray exam
- A CT Scan in Children can be used to diagnose cardiovascular diseases, infectious diseases, cancers, appendicitis, and many other disorders
What part of the Body does the Procedure involve?
The CT Scan in Children involves the soft tissues, blood vessels, internal organs, and bones.
Why is the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure Performed?
CT Scans in Children are performed for the following reasons:
- In emergency situations, to examine children in motor vehicle accidents or with serious injuries, such as affecting their chest, abdomen, pelvis, and to examine children having difficulty breathing
- To identify pulmonary embolism, abdominal aortic aneurysms, various cancers and tumors, and many other vascular diseases
- To diagnose various injuries of skeletal structures, since a CT scan can even show very small bones, muscles and the blood vessels surrounding it
- To diagnose kidney tumors, neuroblastoma, cystic fibrosis, appendicitis, inflammatory bowel disease, lymphoma, and malformations of the kidneys, blood vessels, and heart
- To evaluate trauma to blood vessels or lungs, birth defects, complications from infections, airway diseases, and some tumors of the lungs
- To measure bone density
- A CT scan can be used to guide biopsy needles to the target organs
- Minimally-invasive tumor treatments and radiation treatment for tumors also use CT for guidance
- To evaluate kidney stones, tumors/cysts of ovary, problems with the bladder, or any other disease associated with pelvic region
- To check the result of a gastric bypass, an organ transplant, surgery, and chemotherapy
What is the Equipment used? (Description of Equipment)
The equipment for a Pediatric CT Scan consists of:
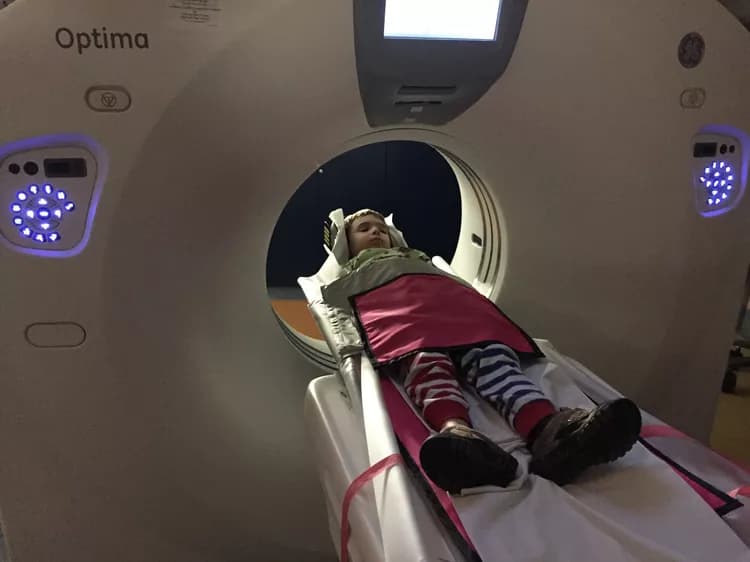
- A CT scanner that appears like a big box with a hole inside
- The examination table on which the patient lies down; the table slides into the hole during the procedure
- X-ray tube and electronic X-ray detectors that rotates around the patient
- Images are taken from a computer
A transducer (part of the scanner) is used to send high frequency sound waves in the body and the computer creates the images, based on the echoes of that sound returning from the patient’s body.
What are the Recent Advances in the Procedure?
There have been no recent advances to replace the Children’s CT Scan procedure.
What is the Cost of performing the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure?
The cost of CT Scan in Children depends on a variety of factors, such as the type of your health insurance, annual deductibles, co-pay requirements, out-of-network and in-network of your healthcare providers and healthcare facilities.
In many cases, an estimate may be provided before the procedure. The final amount depends upon the findings during the surgery/procedure and post-operative care that is necessary.
When do you need a Second Opinion, prior to the Procedure?
- It is normal for a patient to feel uncomfortable and confused with a sudden inflow of information regarding Children’s CT Scan procedure and what needs to be done
- If the patient needs further reassurance or a second opinion, a physician will almost always assist in recommending another physician
- Also, if the procedure involves multiple steps or has many alternatives, the patient may take a second opinion to understand and choose the best one. They can also choose to approach another physician independently
What are some Helpful Resources?
http://www.radiologyinfo.org/en/info.cfm?pg=pedia-ct (accessed on 08/02/2014)
Prior to Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure:
How does the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure work?
- A CT scan is very similar to taking an X-ray. In an X-ray, radiation passes through the body and an image is recorded on photographic film. The bones appear white, air appears black, and soft tissues appear as gray patches
- In the CT scan, electronic X-ray detectors and X-ray beams rotate (around the patient) and measure the amount of radiation absorbed
- The X-ray beam in a CT scan follows a spiral path, as the examination table is moving through the scanner
- A two-dimensional, cross sectional image of the body is created by a computer program, by utilizing all the data generated by the scanner. The CT scan produces a very detailed multidimensional view of the body’s interior regions
- The Children's (Pediatric) CT produces images of the body, in a way as can be compared to looking at a loaf of bread, by cutting the loaf into thin slices
- With an advanced detector technology, current CT scanners can obtain multiple slices in just one rotation. Such types of CT scanners are called “multislice CT” or “multidetector CT”
- Advanced CT scanners can scan large sections of body in a very short time (like a few seconds). They can be adjusted to reduce the radiation dose too
How is the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure Performed?
The Computed Tomography (CT) - Children procedure is performed in the following manner:
- During the test, the patient is asked to lay flat on their back, side, or stomach, during the examination
- As any motion may affect the quality of examination, the patients are asked to stay still on the table; young children may be given a sedation, to keep them still
- In many exams, a contrast material is also used, which is injected through an IV, or is swallowed, or administered by enema
- The child is moved rapidly through the scanner
Where is the Procedure Performed?
A Pediatric CT Scan is performed as an outpatient procedure, at a hospital.
Who Performs the Procedure?
A Children’s CT Scan is usually performed by a radiology technologist.
How long will the Procedure take?
The CT Scan in Children will take about 30-60 minutes.
Who interprets the Result?
A radiologist interprets the results of the CT Scan in Children.
What Preparations are needed, prior to the Procedure?
The following preparations may be needed prior to a CT Scan in Children:
- The physician may evaluate the individual’s medical history to gain a comprehensive knowledge of the overall health status of the patient, including information related to the medications that are being currently taken
- Do inform the medical professional if you have a history of any medical conditions, such as a heart disease, asthma, diabetes, or kidney disease
- Do inform the medical professional about any allergies, especially related to barium or iodinated contrast material, which may be used in the procedure
- It is advisable to wear comfortable and loose clothes. Avoid wearing any metal objects or jewelry, as it may interfere with the x-ray
- The patient must avoid eating or drinking at least 8 hours prior to the procedure, depending on when the procedure is arranged
- Depending on the procedure adopted, the patient may be asked for certain bowel or bladder preparations, before the preparation sessions
What is the Consent Process before the Procedure?
A physician will request your consent for a Computed Tomography (CT) Scan in Children using an Informed Consent Form.
Consent for the Procedure: A “consent” is your approval to undergo a procedure. A consent form is signed after the risks and benefits of the procedure, and alternative treatment options, are discussed. This process is called informed consent.
You must sign the forms only after you are totally satisfied with the answers to your questions. In case of minors and individuals unable to personally give their consent, the individual’s legal guardian or next of kin, shall give their consent for the procedure.
What are the Benefits versus Risks, for this Procedure?
Following are the benefits of the CT Scan in Children:
- A CT scan is a painless, noninvasive procedure; it does not have any side effects
- It can take images of the soft tissues, bones, and blood vessels, at the same time
- A CT scan may be used, even if the patient has an implanted medical device
- CT scanning is a very accurate modality, hence it eliminates the need of having other diagnostic procedures
- It is also very useful in emergencies, helping to quickly identify any internal injuries and bleeding
- Unlike MRI, it is less movement-sensitive (the patients are generally asked to remain very still, while the test is under progress, for both a CT scan and an MRI scan as well)
- A CT scan produces real-time imaging. It can be used for guiding needle biopsies and needle aspirations
- This procedure is very fast and accurate. Thus, it can be used to diagnose pain caused by infections and inflammations, as there is no risk of rupturing diverticulum or bursting appendix and spreading the infection in the body
Following are the risks of the CT Scan in Children:
- Over-exposure to radiation in a CT scan procedure may cause cancer. But, generally the chances of developing cancer is very remote
- CT scanning is recommended for children, only if it is absolutely necessary, as children are very sensitive to radiation
What are the Limitations of the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure?
Following are the limitations of the CT Scan in Children procedure:
- The procedure is not recommended for patients with kidney problems or diabetes.
- An MRI scan is recommended over a CT scan for conditions related to the soft tissues, tissues around the joints, etc.
What are some Questions for your Physician?
Some of the basic questions that you might ask your healthcare provider or physician are as follows:
- What is the Children's (Pediatric) CT procedure?
- Why is this procedure necessary? How will it help?
- How soon should I get it done? Is it an emergency?
- Who are the medical personnel involved in this procedure?
- Where is the procedure performed?
- What are the risks while performing the procedure?
- What are the complications that might take place, during recovery?
- What are the possible side effects from the procedure? How can I minimize these side effects?
- How long will it take to recover? When can I resume normal work?
- How many such procedures have you (the physician) performed?
- Are there any follow-up tests, periodic visits to the healthcare facility required, after the procedure?
- Is there any medication that needs to be taken for life, after the procedure?
- What are the costs involved?
During the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure:
What is to be expected during the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure?
The following may be expected during a Children's (Pediatric) CT procedure:
- There is no pain involved with this procedure
- There might be some noise of the device, as involved with any regular machine function
- The individual may experience some anxiety, due to the noise of the machine, or from staying still for a long time, but no scan associated pain may be felt
- Children, who are sedated, do not feel anything
What kind of Anesthesia is given, during the Procedure?
Generally, no anesthesia is given during the Children's (Pediatric) CT scan procedure. However, in some cases sedation or even general anesthesia may be needed.
How much Blood will you lose, during the Procedure?
There is no blood loss involved during the Children's (Pediatric) CT scan procedure.
What are the possible Risks and Complications during the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure?
- Over-exposure to radiation in a CT Scan of Chest procedure may cause cancer; however, such a risk is very low
- There is a rare chance of developing an allergic reaction, due to the contrast material containing iodine used in the CT scan
- CT scanning is recommended for children, only if it is absolutely necessary, as children are very radiation-sensitive
What Post-Operative Care is needed at the Healthcare Facility after the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure?
There is no postoperative care necessary after a Children's (Pediatric) CT scan procedure.
After the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure:
What is to be expected after the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure?
Generally, no complications or side effects are observed after the CT Scan in Children.
When do you need to call your Physician?
If the patient is experiencing an allergic reaction from the contrast material, then do contact the physician.
What Post-Operative Care is needed at Home after the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure?
There is no postoperative care necessary after the Pediatric CT scan procedure.
How long does it normally take to fully recover, from the Procedure?
The patient needs no recovery time after the Pediatric CT scan procedure.
Additional Information:
What happens to tissue (if any), taken out during the Procedure?
No tissue is extracted from the patient during a Children’s CT Scan.
When should you expect results from the pathologist regarding tissue taken out, during the Procedure?
Since no tissue is removed during the procedure, a pathologist does not get involved in the care of the patient.
Who will you receive a Bill from, after the Computed Tomography (CT) scan in Children radiology procedure?
It is important to note that the number of bills that the patient may receive depends on the arrangement the healthcare facility has with the physician and other healthcare providers.
Sometimes, the patient may get a single bill that includes the healthcare facility and the consultant physician charges. Sometimes, the patient might get multiple bills depending on the healthcare provider involved. For instance, the patient may get a bill from:
- The hospital, where the procedure is performed
- A radiologist, performing the procedure
- Healthcare providers, physicians, who are involved in the process
The patient is advised to inquire and confirm the type of billing, before the Computed Tomography (CT) Scan in Children procedure is performed.
Related Articles
Test Your Knowledge
Asked by users
Related Centers
Related Specialties
Related Physicians
Related Procedures
Related Resources
Join DoveHubs
and connect with fellow professionals

0 Comments
Please log in to post a comment.